




Velvetleaf
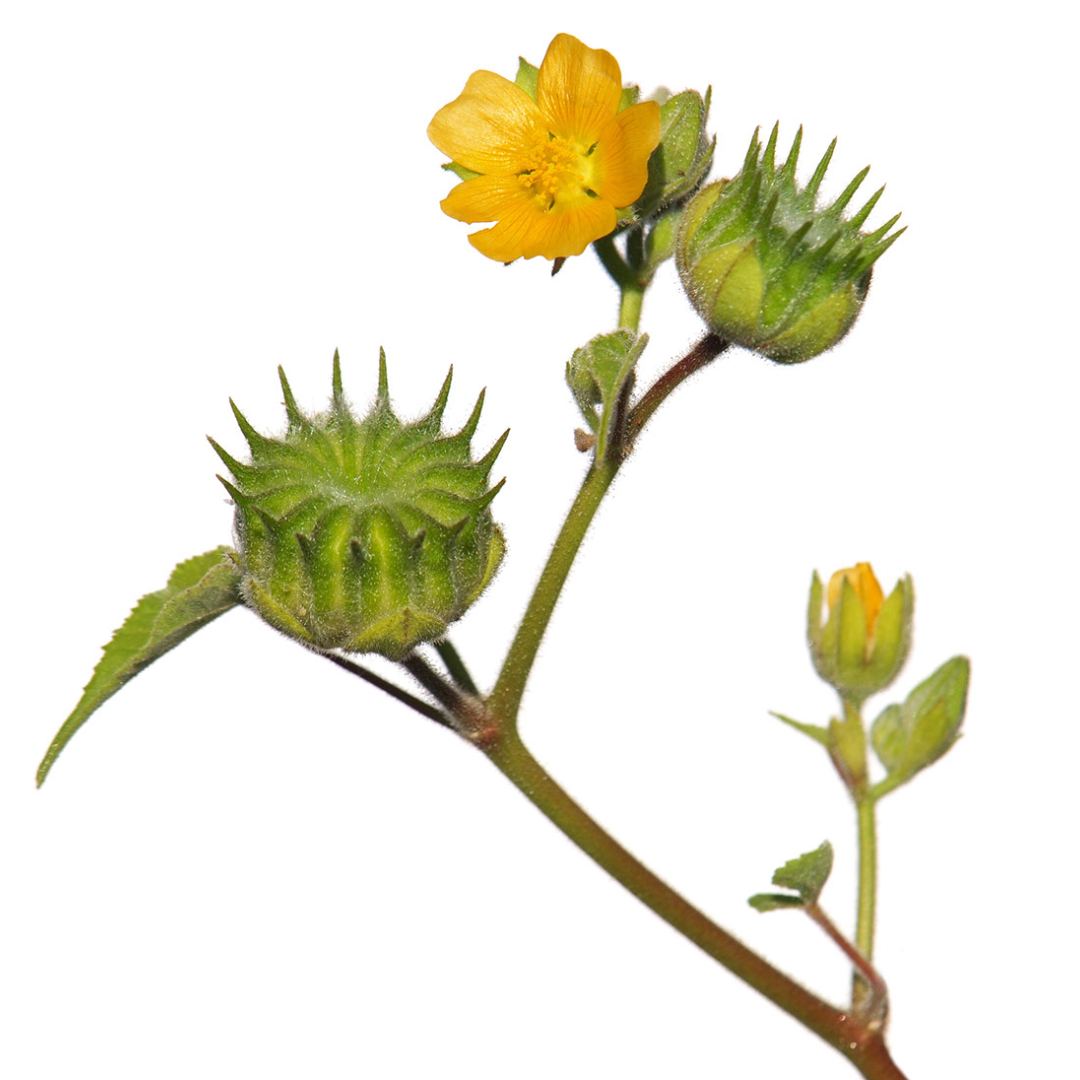
DESCRIPTION: Velvetleaf is a plant with big, soft, and fuzzy leaves that feel like velvet to the touch. The leaves are heart-shaped and can grow up to several inches wide. The plant itself can grow quite tall, sometimes reaching up to 6 feet in height. Its flowers are bright yellow and can bloom throughout the summer. While the plant may look pretty, it is considered a weed by many farmers because it can compete with crops for nutrients and water.
SCIENTIFIC NAME: Abutilon theophrasti
OTHER NAMES: China Jute, Indian Mallow, Buttonweed, Butterprint, Velvetweed
LEAF TYPE: Broadleaf
FLOWERS: Velvetleaf produces bright and showy yellow flowers that are shaped like bells or funnels. The flowers have five petals and are usually around 2-3 inches in diameter. They can grow individually or in clusters on long stalks. When in bloom, the flowers can add a pop of color to the surrounding landscape. However, they are also a sign that the plant is reproducing and spreading its seeds, which can be a problem for farmers trying to grow crops.
LEAVES: Velvetleaf has large, soft, and velvety leaves that are usually heart-shaped and have a pointed tip. They can grow up to several inches wide and long and are covered with fine hairs that give them a fuzzy texture. The leaves are a bright green color and have distinct veins running through them. When the sun shines on the leaves, they can look shiny or glossy. Despite their soft and fuzzy appearance, the leaves can be quite tough and durable, allowing the plant to withstand harsh weather conditions.
LIFE CYCLE: Annual
HOW TO IDENTIFY: Velvetleaf can be identified by its tall and erect stem, large heart-shaped leaves with a fuzzy texture, and bright yellow bell-shaped flowers. The plant can grow up to 6 feet tall and can have multiple branches with leaves and flowers growing out of them. Its leaves are a bright green color and have a velvety texture that makes them feel soft to the touch. The flowers are quite showy and can be seen blooming in the summer months. When in doubt, you can also look for the plant's distinctive seed pods, which are round and flat with several compartments and look like little disks.
MECHANICAL CONTROL RECOMMENDATIONS:
1. Hand pulling - More Info
2. Mowing - More Info
3. Tilling - More Info
4. Mulching - More Info
5. Solarization - More Info
6. Flaming - More Info
7. Mechanical Removal Tools - More Info
8. Grazing - More Info
CHEMISTRY RECOMMENDATIONS:
"Pre-emergent herbicides:
Atrazine: Atrazine is a widely used pre-emergent herbicide that can help control broadleaf and grassy weeds. It's often used in corn and sorghum fields.
Metolachlor (Dual Magnum): Metolachlor is effective against many annual grasses and some broadleaf weeds. It's commonly used in corn, soybean, and other crops.
Isoxaben: Isoxaben is a pre-emergent herbicide used to control broadleaf weeds in ornamental landscapes, nurseries, and other non-crop areas.
Flumioxazin: Flumioxazin is used for broad-spectrum pre-emergent weed control in various crops and non-crop areas. It's effective against a range of broadleaf and grassy weeds.
Pendimethalin: Pendimethalin is used to control annual grasses and some broadleaf weeds in a variety of crops including corn, soybeans, and vegetables.
S-metolachlor (Dual II Magnum): This herbicide is similar to metolachlor and provides pre-emergent control of grasses and some broadleaf weeds.
Dithiopyr: Dithiopyr is used in turfgrass and ornamental settings to control both pre-emergent and post-emergent broadleaf and grassy weeds.
Prodiamine: Prodiamine is commonly used in turfgrass management to prevent the germination of various annual grasses and broadleaf weeds.
Oxadiazon: Oxadiazon is used for pre-emergent weed control in turfgrass, ornamentals, and non-crop areas.
Post-emergent herbicides:
2,4-D: 2,4-D is a widely used selective herbicide for controlling broadleaf weeds in various crops, lawns, and non-crop areas.
Dicamba: Dicamba is another selective herbicide effective against broadleaf weeds. It's commonly used in combination with other herbicides for enhanced weed control.
Glyphosate: Glyphosate is a non-selective herbicide used to control a wide range of weeds, including Abutilon theophrasti. It's used in various crops, landscapes, and non-crop areas.
Clopyralid: Clopyralid is effective against certain broadleaf weeds and is commonly used in turfgrass and non-crop areas.
Fluroxypyr: Fluroxypyr is used for controlling broadleaf weeds in various crops, pastures, and non-crop areas.
Triclopyr: Triclopyr is effective against a range of broadleaf weeds and woody plants. It's often used in forestry, range, and pasture settings.
Carfentrazone: Carfentrazone is used to control broadleaf weeds in turfgrass and non-crop areas. It's often included in herbicide mixtures.
Metsulfuron-methyl: Metsulfuron-methyl is used to control a variety of broadleaf and grassy weeds in turfgrass, non-crop areas, and some crops.
Sulfosulfuron: Sulfosulfuron is used to control grass and broadleaf weeds in crops like wheat, barley, and rice.
Selective herbicides:
2,4-D: A widely used selective herbicide for controlling broadleaf weeds in various crops, lawns, and non-crop areas.
Dicamba: Effective against broadleaf weeds, dicamba is commonly used in combination with other herbicides to enhance weed control.
Clopyralid: Effective against certain broadleaf weeds, clopyralid is used in turfgrass and non-crop areas.
MCPA: Used for controlling broadleaf weeds in various crops and non-crop areas.
Triclopyr: Effective against a range of broadleaf weeds and woody plants, often used in forestry, range, and pasture settings.
Fluroxypyr: Used for controlling broadleaf weeds in various crops, pastures, and non-crop areas.
Aminopyralid: Used to control certain broadleaf weeds, especially those with deep root systems. Commonly used in pastures and non-crop areas.
Quinclorac: Selective herbicide effective against both grassy and broadleaf weeds, commonly used in turfgrass and some crops.
Carfentrazone: Used to control broadleaf weeds in turfgrass and non-crop areas, often included in herbicide mixtures.
Mesotrione: Effective against a variety of broadleaf weeds, used in turfgrass and some crops.
Halauxifen-methyl: A newer herbicide used for selective control of certain broadleaf weeds in cereal crops.
Non-Selective herbicides:
Glyphosate: One of the most widely used non-selective herbicides, effective against a broad spectrum of plants. It's used in various settings, including agriculture, landscaping, and non-crop areas.
Glufosinate: Another non-selective herbicide effective against a wide range of plants. It's used in agricultural and non-crop areas.
Paraquat: A fast-acting non-selective herbicide used to desiccate and control vegetation before planting or in non-crop areas.
Diquat: Diquat is used for desiccation and control of aquatic and terrestrial plants in non-crop areas.
Pelargonic Acid: Also known as ""horticultural vinegar"" or ""vinegar herbicide,"" pelargonic acid-based products act as non-selective contact herbicides that can damage plant tissues upon contact.
Sethoxydim: While primarily a grass-selective herbicide, when used at higher rates, sethoxydim can also have non-selective activity against broadleaf weeds.
Ammonium Nonanoate: This is another non-selective herbicide often used in organic and sustainable farming systems for controlling weeds.
Flame Weeding: While not a herbicide, flame weeding involves using propane torches to quickly heat and kill plants. It's a non-chemical method for non-selective weed control.
Recommended Prevention
Recommended Control

