



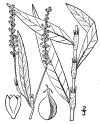
Smartweed
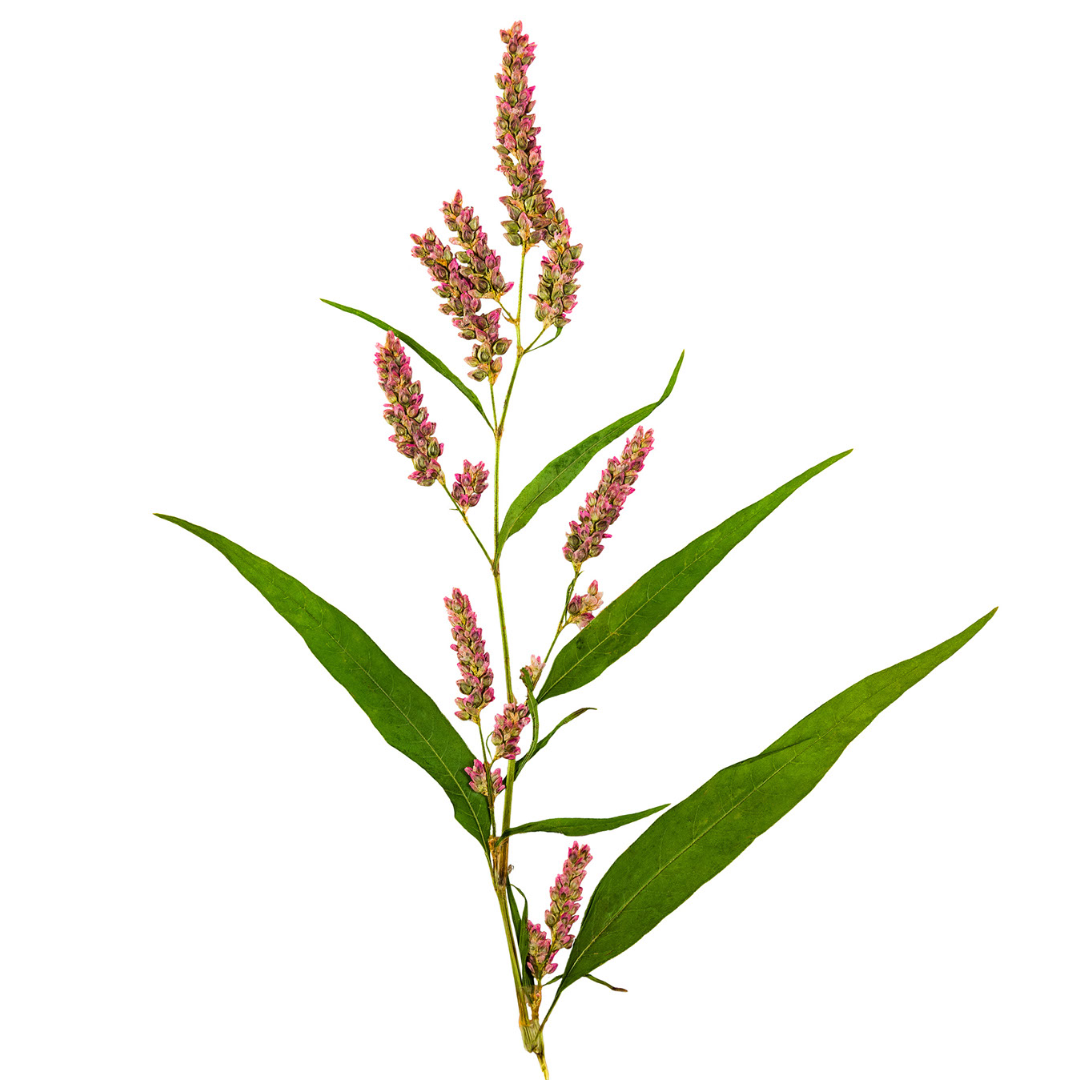
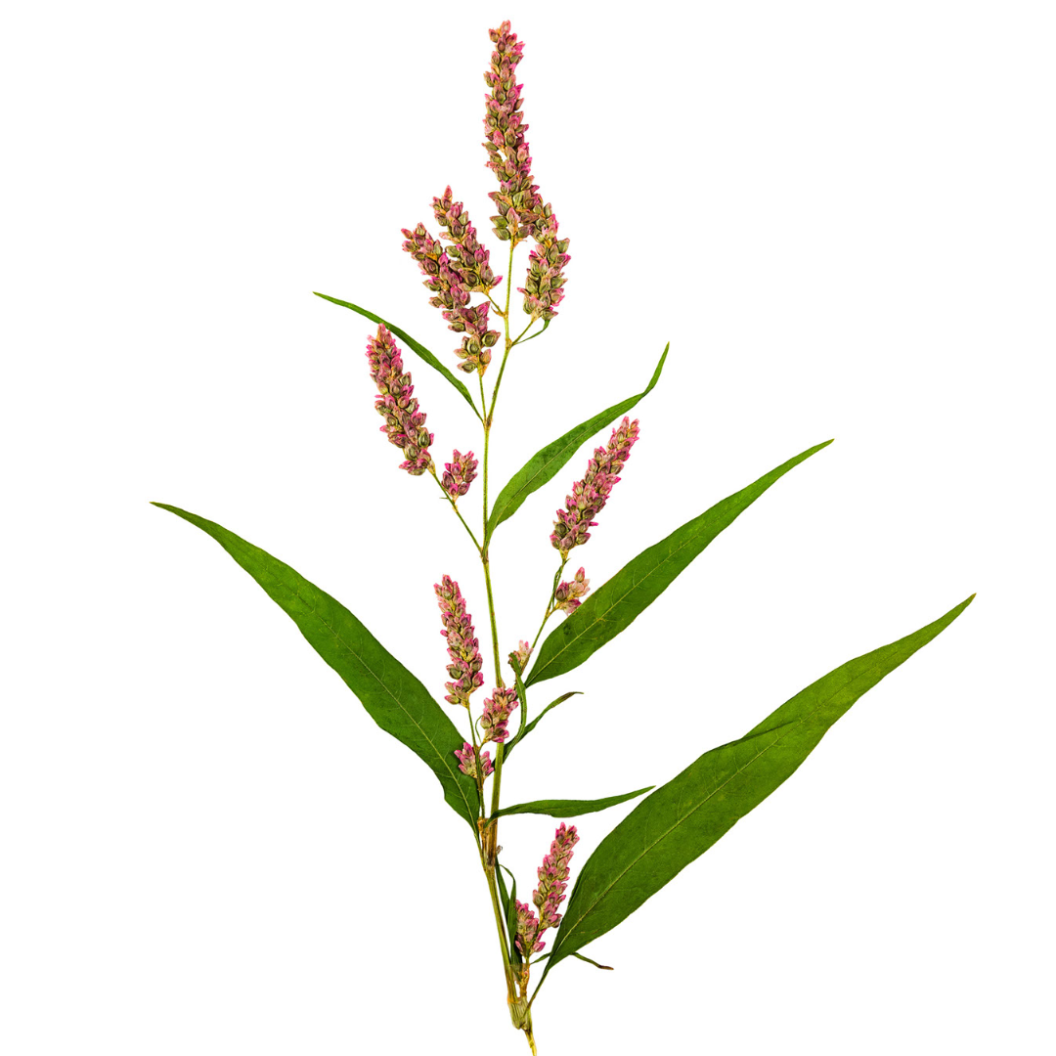
DESCRIPTION: Smartweed is a plant that grows in damp areas like wetlands, marshes, and the banks of streams or ponds. It's a green, leafy plant that can grow up to 3 feet tall. When you touch or crush the leaves, they have a spicy or peppery smell. The flowers are small and pink or white and grow in clusters on the stems. It's called "smartweed" because it was once believed that the plant could improve brain function. Smartweed has been used for centuries as an herbal remedy for various ailments such as inflammation and pain. It is also a food source for ducks and geese.
SCIENTIFIC NAME: Polygonum hydropiperoides
OTHER NAMES: Water Pepper, Knotweed, Biting Knotweed, Mild Water Pepper, Swamp Smartweed, Pinkweed, Redshank, Persicaria, Lady's Thumb, Spotted Lady's Thumb
LEAF TYPE: Broadleaf
FLOWERS: Smartweed flowers are small and delicate, with a pink or white color. They grow in clusters on long stems that rise above the plant's leaves. The flowers are made up of several tiny petals that form a shape similar to a teardrop or oval. When in bloom, these clusters of flowers can create a beautiful and eye-catching display. Smartweed flowers attract bees and other pollinators that help the plant reproduce. After pollination, the flowers give way to small seeds that are dispersed by the wind and water, allowing the plant to spread and grow in new areas.
LEAVES: Smartweed leaves are green and oval-shaped, with pointed tips and smooth edges. They can grow up to a few inches long and are arranged alternately on the stem of the plant. When you touch or crush the leaves, they emit a spicy or peppery smell, which is why the plant is sometimes called "pepperweed". The leaves have a slightly glossy texture and are attached to the stem by a short, slender stalk. Smartweed leaves can vary in size and shape depending on the specific species and growth conditions, but they all share the characteristic spicy scent when disturbed.
LIFE CYCLE: Annual & Perennial
HOW TO IDENTIFY: Smartweed is a plant that can be identified by several characteristics. It tends to grow in wet or damp areas such as marshes, swamps, and the edges of streams or ponds. Look for green and oval-shaped leaves with a pointed tip and smooth edges. When you touch or crush the leaves, they emit a spicy or peppery smell. Smartweed produces small and delicate flowers in clusters that are pink or white in color and have several tiny petals that form a teardrop or oval shape. The stem of smartweed is usually green or reddish-brown, slender, and can grow up to several feet tall.
MECHANICAL CONTROL RECOMMENDATIONS:
1. Hand pulling - More Info
2. Mowing or Cutting - More Info
3. Tilling - More Info
4. Smothering - More Info
5. Flooding - More Info
6. Grazing - More Info
7. Mechanical Removal Tools - More Info
8. Mechanical Harvesting - More Info
CHEMISTRY RECOMMENDATIONS:
"Pre-emergent herbicides:
Trifluralin: This is a selective pre-emergent herbicide used to control a wide range of annual grasses and broadleaf weeds. It's often applied to the soil before weed seeds germinate.
Oryzalin: Oryzalin is another pre-emergent herbicide that targets a variety of annual grasses and broadleaf weeds. It's often used in turf and landscape settings.
Prodiamine: This herbicide is commonly used to prevent the germination of broadleaf weeds and grasses. It's often applied to lawns, golf courses, and ornamental landscapes.
Isoxaben: Isoxaben is a pre-emergent herbicide used to control broadleaf weeds in landscapes, nurseries, and non-crop areas. It can provide some suppression of certain broadleaf weeds.
Dithiopyr: While dithiopyr is primarily used for grassy weed control, it can also offer some control of certain broadleaf weeds. It's used in lawns and turf areas.
Benefin: Benefin is a pre-emergent herbicide that targets grassy and broadleaf weeds. It's often used in lawns and turf settings.
Post-emergent herbicides:
2,4-D: This is a common post-emergent herbicide that targets broadleaf weeds. It's often used in lawns, pastures, and non-crop areas.
Dicamba: Dicamba is another broadleaf herbicide used for post-emergent control of various broadleaf weeds. It's used in a variety of settings, including lawns and agricultural fields.
Clopyralid: Clopyralid is effective against many broadleaf weeds and is often used in turf and non-crop areas. It might provide some control for Polygonum hydropiperoides.
Triclopyr: Triclopyr is used to control a wide range of broadleaf weeds and woody plants. It's applied to various settings, including lawns, pastures, and industrial sites.
Metsulfuron-methyl: While primarily used for controlling grassy weeds, this herbicide might offer some suppression of certain broadleaf weeds, including Polygonum hydropiperoides.
Glyphosate: Glyphosate is a non-selective herbicide that can control a wide range of plants, including broadleaf weeds. However, it should be used with caution, as it can harm non-target plants.
Selective herbicides:
2,4-D: This is a widely used selective herbicide that targets many broadleaf weeds while leaving grasses largely unaffected. It's used in various settings, including lawns, pastures, and non-crop areas.
Triclopyr: Triclopyr is effective against many broadleaf weeds and woody plants. It's often used in turf, rights-of-way, and industrial sites.
Clopyralid: Clopyralid is selective for broadleaf weeds and is commonly used in turf and non-crop areas.
MCPA: MCPA is another selective herbicide used to control various broadleaf weeds in grassy areas.
Chlorsulfuron: While primarily used for controlling grassy weeds, chlorsulfuron might provide some suppression of certain broadleaf weeds.
Aminopyralid: Aminopyralid is used to control a wide range of broadleaf weeds, including invasive and noxious species. It's often used in pastures, rangeland, and non-crop areas.
Quinclorac: Quinclorac is effective against many broadleaf weeds, including those in turfgrass areas.
Non-Selective herbicides:
Glyphosate: Glyphosate is one of the most widely used non-selective herbicides. It kills a broad range of plants by interfering with their ability to produce essential proteins. It's commonly used for large-scale vegetation control and in areas where reseeding or planting new vegetation is planned after treatment.
Glufosinate: Glufosinate is another non-selective herbicide that disrupts plant metabolism and is effective against a variety of weeds. It's often used in non-crop areas, such as industrial sites and along roadsides.
Diquat: Diquat is a contact herbicide that rapidly affects plant cells upon contact. It's often used for controlling emergent aquatic and terrestrial weeds in areas like ponds, lakes, and along waterways.
Paraquat: Paraquat is a fast-acting contact herbicide that affects plant tissues upon contact. It's often used in agricultural and non-crop areas.
Imazapyr: Imazapyr is a herbicide used for long-lasting control of a broad spectrum of plants. It's often used in non-crop areas like rights-of-way and industrial sites.
Recommended Prevention
Recommended Control

