


Knotweed
DESCRIPTION: Knotweed is the common name given to a genus named Polygonum that includes around 130 different species that are almost all commonly referred to as knotweed or buckwheat. The most common species in the United States is the Japanese knotweed. This plant, native to East Asia, was introduced to North American in the late 1800s as an ornamental plant. It has since spread across the U.S., especially the Northeast and Pacific Northwest, where it can outcompete native vegetation, damage infrastructure, and negatively impact entire ecosystems.
SCIENTIFIC NAME: Polygonum cuspidatum or Fallopia japonica
OTHER NAMES: Japanese Knotweed, Mexican Bamboo, Japanese Bamboo, Fleeceflower, Himalayan Fleece Vine
LEAF TYPE: Broadleaf
FLOWERS: Knotweed flowers are small, delicate, and typically white or pink in color. They grow in elongated clusters that look similar to a feather duster and can be several inches long. The clusters usually appear at the tip of the plant's stem or where the leaves join the stem. The flowers bloom in late summer to early fall and create a visually appealing display, which is likely the primary reason they were initially introduced to North America as ornamental plants.
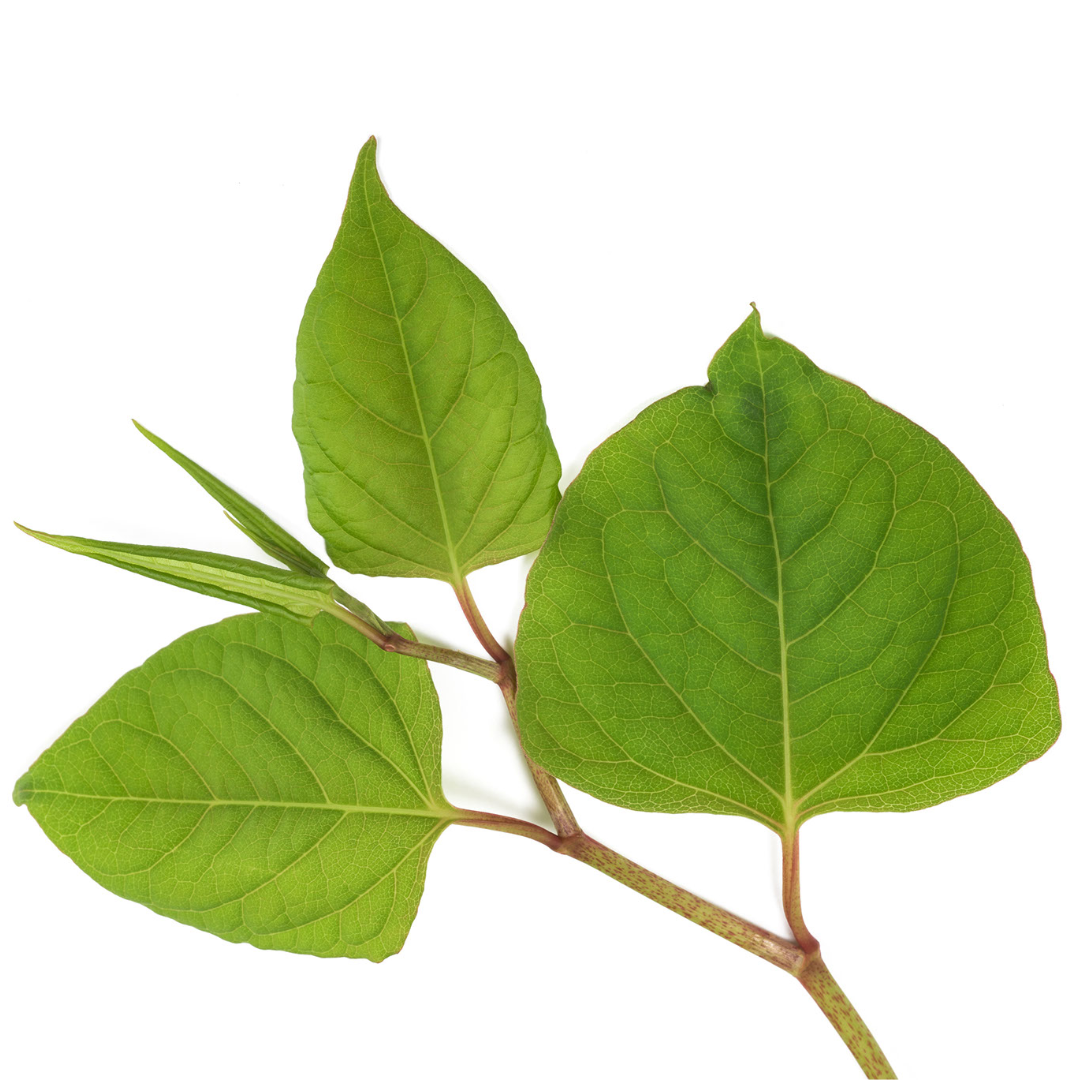
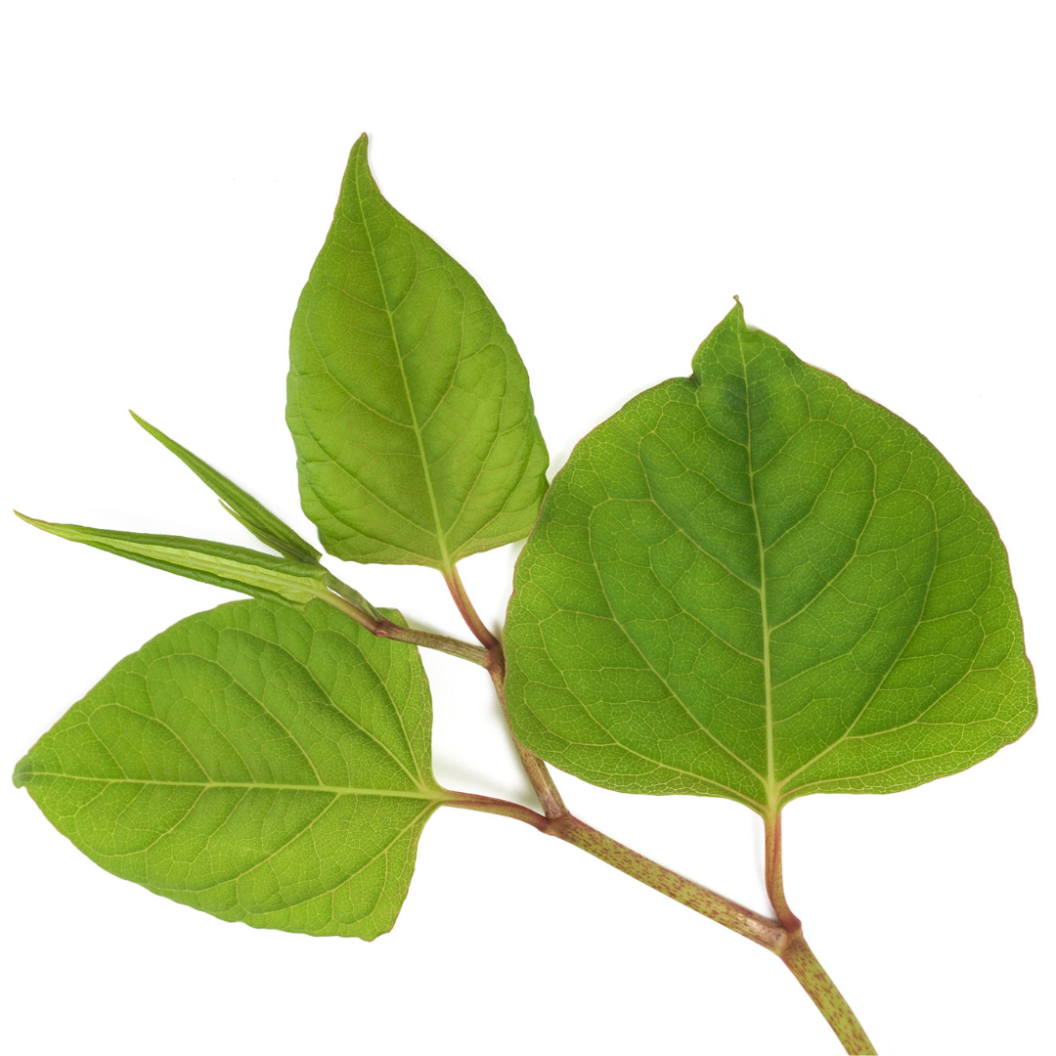
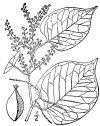
LEAVES: Knotweed leaves are generally lare, broad, and somwhat heart or oval shaped, with a pointed tip. The edges are typically smoth without any tooth-like serrations. Depending on which exact species, the leaves can vary in size and shape, but they will all have an elongated spade-like appearance. They grow alternately along the stems, rather than in pairs opposite each other. They are typically green on both sides with a somewhat glossy or shiny appearance on the upper side.
LIFE CYCLE: Perennial
HOW TO IDENTIFY: Look for tall (up to 10 feet), bamboo-like stems with green spade or shield-shaped leaves. The stems are typically hollow and have distinctive purple speckles. The leaves attach to the stem I na zigzag pattern. When it blooms, the plant produces small, creamy-white or light-pink flowers in clusters that resemble a feather duster.
MECHANICAL CONTROL RECOMMENDATIONS:
1. Cutting and Mowing - More Info
2. Tilling and Digging - More Info
3. Smothering - More Info
4. Grazing - More Info
5. Burning - More Info
6. Steam Treatment - More Info
7. Rhizome Barrier - More Info
8. Mechanical Excavation - More Info
CHEMISTRY RECOMMENDATIONS:
"Pre-emergent herbicides:
Oryzalin: Oryzalin is a pre-emergent herbicide that can be effective against Japanese knotweed and similar invasive plants. It works by inhibiting cell division in germinating seeds.
Isoxaben: Isoxaben is a pre-emergent herbicide that works by inhibiting cell wall synthesis in emerging plants. It can be effective in preventing the growth of Japanese knotweed.
Prodiamine: Prodiamine is a pre-emergent herbicide that forms a barrier in the soil, preventing the germination of weed seeds. It can be effective against Japanese knotweed and other invasive plants.
Dithiopyr: Dithiopyr is a pre-emergent herbicide that prevents cell division in germinating seeds. It can provide control over a range of broadleaf and grassy weeds, including invasive species.
Pendimethalin: Pendimethalin is a pre-emergent herbicide that works by inhibiting cell division in germinating plants. It can help control Japanese knotweed and other invasive species.
Tebuthiuron: Tebuthiuron is a pre-emergent herbicide that can be used for controlling Japanese knotweed and other woody invasive plants. It's important to use this herbicide with caution, as it can have long-lasting effects on the soil.
Post-emergent herbicides:
Glyphosate: Glyphosate is a widely used non-selective herbicide effective for controlling a broad range of plants, including Japanese knotweed. It's systemic, meaning it's absorbed by the plant and travels throughout, eventually killing the entire plant. Use caution near desirable plants, as glyphosate is non-selective.
Triclopyr: Triclopyr is a selective herbicide that targets broadleaf plants, making it a suitable option for controlling Japanese knotweed. It can be used alone or in combination with other herbicides.
Aminopyralid: Aminopyralid is a selective herbicide that targets broadleaf plants. It can provide control over Japanese knotweed and other invasive species. It's commonly used as part of a mixture with other herbicides.
Imazapyr: Imazapyr is a systemic herbicide effective against a wide range of plants, including woody species like Japanese knotweed. It's often used in areas where vegetation needs to be controlled for an extended period.
Fluroxypyr: Fluroxypyr is a selective herbicide used to control broadleaf weeds and plants like Japanese knotweed. It can be effective when applied according to the manufacturer's instructions.
Clopyralid: Clopyralid is a selective herbicide that targets broadleaf plants. It can be used to control invasive species like Japanese knotweed when applied correctly.
2,4-D: 2,4-D is a selective herbicide that targets broadleaf plants. While it might not be as effective as other options for controlling Japanese knotweed, it can still be used in certain situations.
Sulfosulfuron: Sulfosulfuron is a herbicide that targets grassy and broadleaf weeds. It can be effective against Japanese knotweed when used as part of an integrated approach.
Dicamba: Dicamba is a selective herbicide that targets broadleaf plants. It can be used to control Japanese knotweed, but careful application is necessary to avoid damaging non-target plants.
Selective herbicides:
Triclopyr: Triclopyr is a systemic herbicide that targets broadleaf plants. It can be effective in controlling Japanese knotweed while causing minimal damage to grasses and other non-target vegetation.
Aminopyralid: Aminopyralid is a selective herbicide that targets broadleaf plants, making it a suitable option for controlling Japanese knotweed. However, it's important to follow application guidelines to avoid harming desirable plants nearby.
Fluroxypyr: Fluroxypyr is a selective herbicide used to control broadleaf weeds. It can be effective against Japanese knotweed while having lower impacts on grasses.
Clopyralid: Clopyralid is a selective herbicide that targets broadleaf plants and can be used for controlling invasive species like Japanese knotweed. Careful application is essential to prevent damage to non-target plants.
Metsulfuron-methyl: Metsulfuron-methyl is a systemic herbicide effective against a wide range of broadleaf plants, including some invasive species. It can be used for targeted control of Japanese knotweed.
Imazapyr: Imazapyr is a non-selective herbicide but can be used selectively when applied to foliage or injected directly into stems of targeted plants. It's particularly effective for woody invasive plants like Japanese knotweed.
Non-Selective herbicides:
Glyphosate: Glyphosate is one of the most widely used non-selective herbicides. It's effective for killing Japanese knotweed and other invasive plants. Glyphosate works by inhibiting an enzyme necessary for plant growth. However, it can also impact nearby desirable plants if not applied carefully.
Glufosinate: Glufosinate is another non-selective herbicide that can be used to control invasive plants like Japanese knotweed. It disrupts plant cell processes and can be effective when applied according to the manufacturer's instructions.
Paraquat: Paraquat is a fast-acting non-selective herbicide that causes rapid tissue damage in plants. It's effective for controlling a range of invasive species but should be used with extreme caution due to its high toxicity to humans and animals.
Diquat: Diquat is a contact herbicide that causes quick desiccation of plant tissues. It's effective for controlling Japanese knotweed and other invasive plants when applied directly to foliage.
Pelargonic Acid: Pelargonic acid is a fatty acid-based herbicide that burns and desiccates plant tissues on contact. It can be used for controlling invasive plants, but it may require multiple applications.
Imazapyr: Imazapyr is a non-selective herbicide that is particularly effective against woody plants. It can be used for targeted control of Japanese knotweed, especially in areas where other vegetation is not a concern.
Recommended Prevention
Recommended Control

